

Dear Readers,
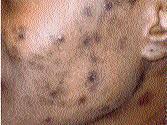
Annmarie, 28, writes Lifeline from Kingston 6. She said she has sensitive skin and is tired of the dark spots left when insects bite her and the dark acne scars on her face and chest. It seems they take a very long time to fade away, if ever. Annmarie is also tired of purchasing expensive prescriptions over many years, which she just cannot afford at this time. She asked Lifeline to suggest home remedies which could help with spot removal.
There are several different causes of skin blemishes and treatment, therefore, will vary.
The chemical, melanin, which gives skin its colour, can produce freckles and dark spots on the skin, especially over sun-exposed areas.
Dark spots can also be caused by hormonal fluctuations (melasma thyroid dysfunction).
Certain drugs can affect skin colour when taken.
Trauma to the skin can result in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (burns, acne and psoriasis).
It is always important to rule out a melanoma, or other form of skin cancer, when looking at new spots on the skin.
Overexposure to UV rays from the sun. Ninety per cent of people over age 60 have 'lentigines', dark spots caused by over-exposure to sunlight. Many younger people also have them.
Melasma should be mentioned as it occurs for some women during menstruation, pregnancy, during menopause, with use of oral contraceptive pills or with thyroid dysfunction. Darker patches can occur on the cheeks and neck of affected individuals.
Knowing the cause of the discoloration allows an individual to properly choose their treatment. For example, avoidance of sun exposure and the use of sunscreen can help sun-related dark spots (lentigines) to disappear.
Hyperpigmentation is a common problem and there are many over-the-counter preparations which can be purchased , which claim to address this problem. However when unsure of the cause, see a dermatologist. Another reason to see a dermatologist is that most of the best treatments for irregular skin hyperpigmentation are prescribed preparations. Also, a dermatologist can rule out more serious causes of skin changes (e.g. skin melanoma).
TYPES OF TREATMENT
When blemishes are new, they may only involve the superficial layers of the skin. This may allow for simple exfoliation of superficial skin to get rid of the marks. Exfoliation is the process of removing the top layer of the skin, bringing a new layer to the surface.
There are several prescribed creams, gels and lotions for topical use (e.g. retinoids and alpha/beta hydroxyl acids), which remove the top layer of skin and allow for fresh growth of new cells. This treatment is applicable for most causes of hyperpigmentation.
Alpha-hydroxyl acids include mandelic acid, citric acid and lactic acid. Beta-hydroxyl acids most commonly refer to salicylic acid, which is a common ingredient of over-the-counter acne medications and skin treatments. Salicylic acid and mandelic acid are both applied as creams, moisturisers or used as a skin peel.
Retinoic acid, or Retin-A, is a form of vitamin A, which is very effective against acne and dark spots. It is available only by prescription as a cream or gel.
Chemical peels can be used in light-complexioned persons to remove the top layers of the skin. When used in dark-skinned individuals, it tends to cause more blemishes and dark areas to appear! Chemical peels can be light, medium or deep. Sometimes a deep chemical peel can leave spots behind, so be careful with this.
Microdermabrasion is a procedure which uses fine crystals to 'sandblast' dark spots. A new layer grows in place of the skin removed and treatments may be required over months.
Laser treatment uses pulses of laser light to destroy dark pigmented spots, allowing new skin to grow. This method is very effective but expensive. Laser treatment is usually best when the spot has been around for a long time, as these spots are usually deep in the skin and not readily treated by the other methods mentioned.
OVER-THE-COUNTER PRODUCTS AND HOME REMEDIES
When looking for an over-the-counter product, try to find one which contains a combination of ingredients: hydroquinone (two percent or less), cucumber, soy, calcium and azelaic acid.
Gently rub the blemished skin with citrus. Citrus fruits contain large amounts of vitamin C (ascorbic acid), which will help to slough off the superficial layer of skin without injury. The citrus juice is applied to the blemish with a cotton ball and left on the face for about 20 minutes, twice a day, until blemishes fade.
Massage dark spots with vitamin E, which repairs damaged cells and strengthens new skin cells. With daily applications, spots often fade.
Aloe vera is an excellent moisturiser and can help fade dark spots. Apply the pulp of the aloe vera directly to dark spots. Aloe vera gel is also available on pharmacy shelves.
Red onions have acidic properties, which lighten dark spots on the skin. Apply for 15 minutes, daily, and wash off.
Limit sun exposure. Exposure to ultra violet rays is a very common cause of dark spots. Always wear sunscreen with a minimum SP factor of 15 or greater. Don't sunbathe! When the tan fades, dark spots might remain behind.
Vinegar is an acid which acts like a mild chemical peel and can be applied for a limited time.
Many people have a dark discoloration around their neck, known of as acanthosis nigricans. It has several causes such as ageing, sun exposure, genetics, poly cystic ovarian syndrome, diabetes and sudden weight loss or gain. Applications of aloe vera daily may help control this condition.
If natural methods don't give the results needed, see a dermatologist. Thick scars below the skin will definitely require professional treatment.
Write to:
Lifeline,
PO Box
1731
KGN 8
AJM
